How Blockchain Works for Absolute Beginners
Introduction
Blockchain is a technology that many people hear about, especially because of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. But what exactly is blockchain, and how does it work? If you’re new to this topic, it might seem confusing or complicated. The good news is, blockchain is easier to understand than you think.
In this article, we will explain blockchain in simple language, step by step. You will learn what blockchain is, how it works, and why it is becoming such an important part of the digital world. Whether you want to understand cryptocurrency or just curious about new technology, this guide is made for absolute beginners like you.
Let’s get started!
What is Blockchain?

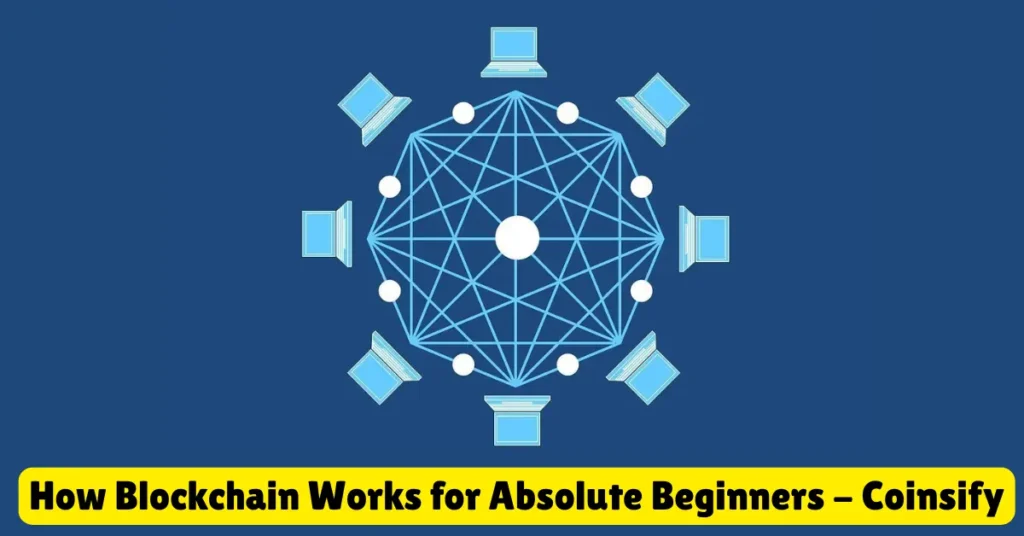
Blockchain is a special kind of database that stores information in a very secure and organized way. Unlike regular databases that store data in tables or files, blockchain stores data in groups called “blocks.” Each block holds a set of information, and these blocks are connected or “chained” together in a specific order, creating a chain of blocks hence the name “blockchain.”
One of the most important things about blockchain is that it is decentralized. This means that instead of one single person or company controlling the data, many different computers (called nodes) around the world share and maintain the same information. This makes blockchain very secure and hard to change or hack.
Blockchain is most famous for being the technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. But its use is much broader now it can be used for keeping records, tracking goods in supply chains, voting systems, and more.
Key Concepts in Blockchain
To understand how blockchain works, it’s important to know a few basic ideas:
Blocks
- A block is like a container that holds information. In the case of cryptocurrencies, a block contains details about transactions such as who sent money to whom, and how much. Each block also has a unique code called a “hash” that identifies it.
Chain
- Blocks are connected in a specific order, one after another. Each block links to the previous block using its hash, forming a chain. This makes sure that the order of transactions is clear and can’t be changed.
Decentralization
- Instead of storing the blockchain on one central computer, many computers (called nodes) around the world store copies of it. This makes the system decentralized and very hard to manipulate because everyone has the same information.
Transparency
- Since many people have copies of the blockchain, the information is visible and can be checked by anyone in the network. This transparency helps build trust.
Immutability
- Once information is added to the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted. This is because changing one block would require changing all the blocks after it, which is nearly impossible.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Understanding how blockchain works is easier if you think about it as a process that happens step by step. Here’s how it works:
Transaction Initiation
- Someone starts a transaction. This could be sending money, recording data, or any information that needs to be shared with the network.
Verification
- The transaction is sent to a network of computers called nodes. These nodes check the details to make sure the transaction is valid. They use special rules to confirm that the sender has the right to make the transaction.
Grouping into a Block
- Once verified, the transaction is grouped together with other transactions waiting at the same time. All these transactions form a block.
Adding the Block to the Chain
- This new block is added to the existing blockchain. It connects to the previous block by including the previous block’s unique hash, linking them together securely.
Updating the Network
- After the block is added, all the computers in the network update their copies of the blockchain. This way, everyone has the same, up-to-date information.
This process happens very quickly and without the need for a central authority, like a bank or government. The power of blockchain lies in this shared, secure system that keeps everything transparent and trustworthy.
Why is Blockchain Secure?

Blockchain is considered very secure because of several important features working together:
Cryptographic Hashing
- Each block has a unique code called a “hash,” created by a special math function. Even a tiny change in the block’s data will change the hash completely, making it easy to spot if someone tries to tamper with the information.
Linking Blocks Together
- Every block contains the hash of the previous block. This means blocks are connected in a chain. If someone tries to change one block, they would have to change the hash in that block and all the blocks after it, which is extremely difficult.
Decentralization and Consensus
- The blockchain is stored on many computers around the world. To add a new block, most of these computers need to agree that the block is valid. This agreement process is called “consensus.” It stops bad actors from adding fake information because they would need to control most of the network.
Consensus Mechanisms
- Different blockchains use different methods to reach consensus, like Proof of Work (used by Bitcoin) or Proof of Stake. These methods make it costly or difficult to cheat the system.
Because of these features, blockchain keeps data safe, reliable, and very hard to hack or change without permission.
Real-Life Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is not just about cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. It has many uses in different fields because of its secure and transparent nature. Here are some important real-life applications:
Finance and Banking
- Blockchain helps make financial transactions faster, cheaper, and more secure. It reduces the need for middlemen like banks, making money transfers more efficient.
Supply Chain Management
- Companies use blockchain to track products from the factory to the customer. This helps verify the authenticity of goods, prevent fraud, and improve transparency.
Voting Systems
- Blockchain can make voting more secure and transparent. It helps prevent cheating by ensuring every vote is recorded correctly and cannot be changed.
Healthcare
- Medical records stored on a blockchain are secure and can be shared easily between authorized doctors and hospitals, improving patient care and privacy.
Real Estate
- Blockchain can simplify property transactions by securely recording ownership and reducing paperwork and fraud.
Digital Identity
- It allows people to control their digital identity securely, reducing identity theft and fraud.
These examples show how blockchain can make many industries safer, more efficient, and more trustworthy.
Common Misconceptions About Blockchain
Even though blockchain is becoming more popular, many people still have some wrong ideas about it. Let’s clear up a few common misconceptions:
Blockchain is the same as Bitcoin
- Bitcoin is just one example of how blockchain technology can be used. Blockchain itself is much broader and can be applied to many areas beyond cryptocurrencies.
Blockchain is completely anonymous
- While blockchain offers privacy, most blockchains are not fully anonymous. Transactions are recorded on a public ledger, so with some effort, identities can sometimes be traced.
Blockchain is unhackable
- Blockchain is very secure, but no system is 100% perfect. However, because of its design, hacking a blockchain is extremely difficult and costly.
Blockchain is only useful for tech experts
- Blockchain can be used by anyone, and many tools and services are making it easier to understand and use without deep technical knowledge.
Blockchain always means no middlemen
- While blockchain can reduce the need for middlemen, some applications still involve trusted third parties to make the system work smoothly.
Understanding these facts helps you see blockchain clearly and avoid confusion.
How Blockchain Works: Step-by-Step Guide for Absolute Beginners
Step 1: Starting a Transaction
- Imagine you want to send money or share some information. This action begins a transaction that needs to be recorded safely.
Step 2: Broadcasting the Transaction
- Your transaction is sent out to a network of computers called nodes. These nodes are spread all over the world and work together to check your transaction.
Step 3: Verifying the Transaction
- The nodes check your transaction to make sure everything is correct. For example, if you’re sending money, they verify that you have enough funds and that the transaction is legitimate.
Step 4: Grouping Transactions into a Block
- Once verified, your transaction is grouped with other transactions that happened around the same time. This group of transactions forms a block.
Step 5: Solving the Puzzle (Consensus Process)
- Before adding the block to the blockchain, the network nodes compete or cooperate to validate the block through a consensus method. For example, in Bitcoin’s blockchain, this is called “Proof of Work,” where computers solve a complex math puzzle.
Step 6: Adding the Block to the Chain
- When the block is validated, it is added to the existing blockchain. This new block connects to the previous block using a unique code called a “hash,” creating a secure chain of blocks.
Step 7: Updating All Copies
- After the block is added, all nodes in the network update their copies of the blockchain to include the new block. This keeps everyone’s data consistent and up to date.
Step 8: Transaction Complete
- Your transaction is now part of the blockchain and can’t be changed or deleted. It’s secure, transparent, and recorded forever.
Common FAQs About Blockchain
What exactly is blockchain?
- Blockchain is a special kind of database that stores information in blocks, which are linked together in a chain. It is secure, transparent, and decentralized.
Is blockchain only used for Bitcoin?
- No, blockchain has many uses beyond Bitcoin. It can be used in finance, healthcare, supply chains, voting, and more.
How is blockchain different from regular databases?
- Unlike regular databases controlled by one person or company, blockchain is decentralized and shared across many computers. This makes it harder to tamper with.
Can anyone change information on the blockchain?
- No, once information is added to the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted. This keeps the data secure and trustworthy.
Is blockchain anonymous?
- Blockchain offers some privacy but is not completely anonymous. Transactions are recorded publicly, but identities are hidden behind codes.
Do I need to be a tech expert to understand blockchain?
- Not at all! Many resources explain blockchain in simple terms, and tools are making it easier for everyone to use.
How safe is blockchain from hacking?
- Blockchain is very secure because of its design, but no system is 100% hack-proof. It is still much harder to hack than traditional systems.
What is a node in blockchain?
- A node is a computer that participates in the blockchain network by storing a copy of the blockchain and helping verify transactions.
What does decentralization mean?
- Decentralization means that no single person or organization controls the blockchain. Instead, many computers work together to keep it running.
Can blockchain replace banks or governments?
- Blockchain can reduce the need for middlemen in some cases, but it is unlikely to completely replace banks or governments anytime soon.
Conclusion
Blockchain is a powerful technology that makes storing and sharing information safe, transparent, and trustworthy. Even though it might sound complicated at first, understanding the basics is easier than you think. Whether it’s for cryptocurrencies or other uses, blockchain is changing how we handle data in many industries. By learning how it works, you’re taking the first step into the future of technology.
Bonus Points About Blockchain
- Blockchain is Growing Fast: Many companies and governments are exploring blockchain technology to improve security and transparency.
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts stored on the blockchain that automatically carry out agreements without needing a middleman.
- Public vs Private Blockchains: Public blockchains are open to everyone, while private blockchains restrict access to certain users or organizations.
- Energy Use Debate: Some blockchains use a lot of energy (like Bitcoin’s Proof of Work), but newer methods like Proof of Stake are more energy-efficient.
- You Don’t Need to Own Cryptocurrency to Use Blockchain: Many blockchain applications don’t require you to buy or use cryptocurrencies.
- Blockchain Can Help Reduce Fraud: Because data can’t be changed easily, blockchain helps prevent fraud in many industries.
- Blockchain is Still Evolving: Technology is constantly improving, so new uses and better versions of blockchain keep emerging.
Also read
- What is a Crypto Wallet and How Does It Work? – Coinsify
- 10 Crypto Terms Every Beginner Must Know – Coinsify
- What is Blockchain Technology – Complete Guide – Coinsify
- How to Buy Crypto Safely in 2025 – Complete Guide – Coinsify
- Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Key Differences Explained – Complete Guide
- Ultimate Blockchain Glossary: Learn Blockchain Terms Easily
- How to Buy Bitcoin Safely (Complete Beginner’s Guide)
- Top 10 Crypto Wallets for Beginners (2025 Edition)
- What is Cryptocurrency? A Beginner-Friendly Guide (2025)